The world of healthcare is on the cusp of a revolution. Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to transform how we diagnose diseases, personalize treatments, and even discover new cures. But this exciting new era also presents significant challenges. This article explores the three key challenges and opportunities that will shape the future of AI in medicine.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: Innovations and Challenges
Artificial intelligence is rapidly changing the landscape of healthcare. From improving diagnostic accuracy to accelerating drug discovery, AI offers tremendous potential to improve patient outcomes and revolutionize the practice of medicine. However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of the ethical, practical, and societal implications of AI in healthcare. In this article, we delve into the innovative applications of AI in medicine, examining the key challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
I. Introduction
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming industries from manufacturing to finance, and healthcare is no exception. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and insights that would be impossible for humans to detect. In medicine, this capability has the potential to revolutionize everything from diagnostics and treatment to drug discovery and patient care. However, the implementation of AI in healthcare also raises important questions about data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the future of the medical profession. This article explores the innovative applications of AI in healthcare, analyzes the key challenges facing its adoption, and discusses the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
II. Innovative Applications of AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is making significant strides across a range of medical applications, transforming how diseases are diagnosed, treated, and even prevented. Here are some key areas where AI is having a profound impact:
Diagnostics:
AI is revolutionizing medical diagnostics by enabling faster, more accurate, and less invasive disease detection. Machine learning algorithms, trained on massive datasets of medical images, can identify subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye.
- Image Analysis: AI-powered systems are now capable of analyzing X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect various conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders, often at earlier stages than traditional methods. For instance, AI algorithms have shown promising results in detecting lung cancer from CT scans, sometimes even surpassing the accuracy of expert radiologists.
- Biomarker and Genetic Analysis: AI is also being used to analyze blood tests, genetic data, and other biomarkers to predict an individual’s risk of developing specific diseases. This allows for proactive interventions and personalized prevention strategies. For example, AI can analyze a patient’s genomic data to identify predispositions to certain cancers or heart conditions, enabling earlier and more targeted screenings.
Personalized Medicine:
The era of “one-size-fits-all” medicine is fading as AI empowers personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, medical history, and other relevant data, AI algorithms can predict their response to different treatments and recommend the most effective options. This personalized approach can lead to better outcomes and fewer adverse effects.
- Predictive Medication Effectiveness: AI can predict how a patient will respond to specific medications, allowing doctors to choose the most effective drugs and avoid those that are likely to cause side effects. This is particularly valuable in areas like oncology, where treatment decisions are complex and have significant consequences. Pharmacogenomics, guided by AI, is playing an increasingly important role in optimizing drug selection.
Drug Discovery:
The traditional drug discovery process is often lengthy, expensive, and prone to failure. AI is accelerating this process by:
- Identifying Drug Candidates: AI algorithms can analyze vast databases of molecular structures and biological data to identify potential drug candidates with a higher likelihood of success. For example, companies like Atomwise are using AI to accelerate the discovery of new drugs by predicting the binding affinity of molecules to target proteins.
- Predicting Efficacy and Safety: Machine learning models can predict the efficacy and safety of drug candidates, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming laboratory experiments. This allows researchers to focus their efforts on the most promising candidates.
Robotic Surgery:
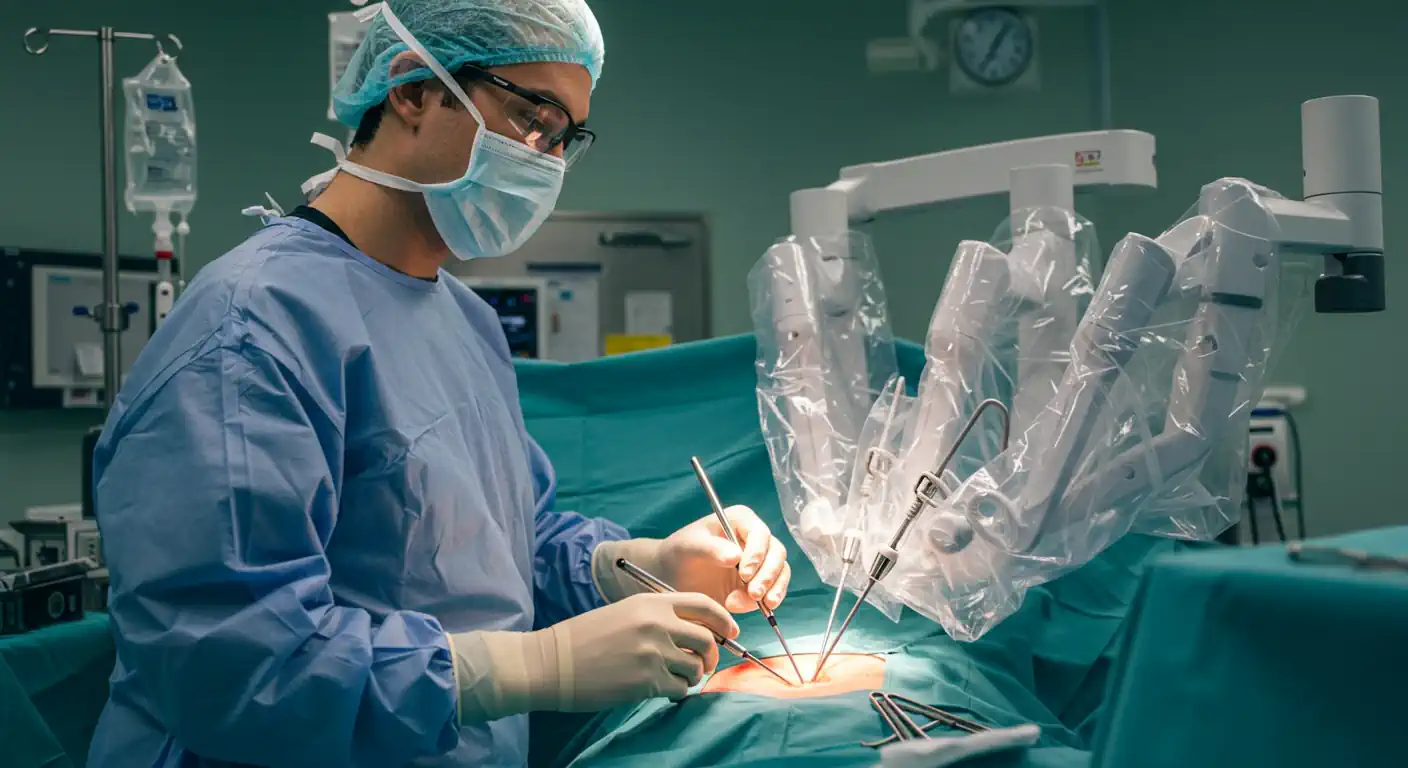
AI-powered robotic surgery systems are enhancing surgical precision and minimizing invasiveness.
- Enhanced Precision and Control: Robotic systems like the da Vinci Surgical System, guided by AI, allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater dexterity, precision, and control, leading to smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery times.
- AI-Assisted Navigation: AI algorithms can assist surgeons in navigating complex anatomical structures, identifying critical landmarks, and minimizing tissue damage. AI can also be used to create 3D models from pre-operative scans, allowing for better surgical planning.
Automation of Administrative Tasks:
AI is streamlining administrative tasks, freeing up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
- Optimized Scheduling and Record Management: AI-powered systems can automate appointment scheduling, manage patient records, and process insurance claims more efficiently than traditional methods.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: By automating routine tasks, AI can reduce the administrative burden on doctors and nurses, allowing them to spend more time with patients and provide better care. AI-powered chatbots, for example, can handle routine patient inquiries and appointment scheduling.
III. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are substantial, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of the ethical and practical challenges that accompany its implementation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for building trust, ensuring patient safety, and maximizing the positive impact of AI in medicine. Here are some of the key hurdles we must overcome:
Data Privacy and Security:
AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of sensitive patient data. Protecting this data from unauthorized access and misuse is paramount.
- Robust Security Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, is essential to safeguard patient information.
- Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare organizations must comply with strict regulations, such as HIPAA in the US, regarding the collection, storage, and use of patient data.
- Data Governance Frameworks: Establishing clear data governance frameworks that outline how data is collected, used, and shared is critical for maintaining patient trust and ensuring responsible data handling.
Bias and Fairness:
AI algorithms can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Representative Datasets: Training AI models on diverse and representative datasets is essential to minimize bias and ensure fairness. If the training data predominantly reflects one demographic group, the AI system may not perform accurately or equitably for other groups.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: Developing methods to detect and mitigate bias in AI algorithms is crucial. This includes techniques for identifying and correcting biased data, as well as developing algorithms that are inherently fair and unbiased.
- Equitable Access: Ensuring that AI-powered healthcare solutions are accessible to all patients, regardless of their background or socioeconomic status, is a crucial consideration.
Transparency and Explainability:
Many AI algorithms operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions. This lack of transparency can hinder trust and adoption.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Developing explainable AI techniques that provide insights into the decision-making processes of AI algorithms is essential for building trust among healthcare professionals and patients. XAI aims to make AI more transparent and understandable.
- Auditing and Validation: Regularly auditing and validating AI systems is critical to ensure their accuracy, reliability, and safety.
Regulatory Approval and Integration:
Bringing AI-powered healthcare solutions to market requires navigating complex regulatory pathways and integrating these technologies into existing healthcare workflows.
- Streamlined Approval Processes: Developing more streamlined and efficient regulatory approval processes for AI-based medical devices and software is crucial for fostering innovation.
- Seamless Integration: Integrating AI systems into existing healthcare IT infrastructure and workflows can be challenging. Standardization and interoperability are key to successful integration.
Ethical Dilemmas:
The use of AI in healthcare raises several ethical dilemmas that must be addressed proactively.
- Patient Autonomy: Ensuring that patients retain control over their healthcare decisions and have the right to refuse AI-based treatments is essential.
- Algorithmic Accountability: Determining who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake is a complex ethical and legal issue. Clear lines of accountability must be established.
- Impact on the Medical Profession: The potential for AI to replace certain tasks currently performed by healthcare professionals raises concerns about job displacement and the future of the medical profession. Careful planning and workforce development are needed to address these concerns.
IV. The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI in healthcare is bright, with the potential to transform medicine in profound ways. Continued advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and other AI subfields promise even more sophisticated and impactful applications. Here are some key trends and possibilities on the horizon:
Personalized and Proactive Care:
AI is paving the way for a future where healthcare is not just reactive but proactive and personalized to individual needs.
- Wearable Devices and Remote Monitoring: AI-powered wearable devices and remote monitoring systems will enable continuous health tracking, providing real-time insights into a patient’s vital signs, activity levels, and other health metrics. This data can be used to detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely interventions and preventing more serious problems.
- AI-Driven Health Coaching: AI-powered virtual assistants and health coaches can provide personalized health advice, tailored exercise plans, and nutritional guidance based on an individual’s unique health profile and goals.
Expanded Access to Care:
AI has the potential to bridge the gap in healthcare access, particularly for patients in remote or underserved areas.
- Telemedicine and AI Assistants: Telemedicine platforms powered by AI can connect patients with specialists and provide remote consultations, regardless of their location. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can also provide basic medical information and triage patients, making healthcare more accessible and affordable.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics in Remote Areas: Portable AI-powered diagnostic devices can be deployed in remote areas, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses even where access to medical facilities is limited.
Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development:

AI will continue to play a crucial role in accelerating the development of new drugs and personalized treatments.
- Target Identification and Drug Design: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of biological data to identify potential drug targets and design new drug molecules with a higher likelihood of success.
- Personalized Drug Development: AI can be used to analyze patient data to identify subgroups that are most likely to benefit from specific treatments, enabling the development of personalized therapies tailored to individual needs.
Integration with Other Advanced Technologies:
The true power of AI in healthcare will be realized through its integration with other cutting-edge technologies.
- Genomics and Biotechnology: Combining AI with genomics and biotechnology will enable a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and lead to the development of more targeted and effective therapies.
- Nanomedicine: Integrating AI with nanomedicine could lead to the development of highly precise and targeted drug delivery systems, revolutionizing how we treat diseases at the cellular level.
The future of AI in healthcare is one of continuous innovation and transformation. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications that will improve patient care, enhance access to healthcare, and ultimately lead to healthier lives for all.
V. Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping the landscape of healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient care, accelerate medical research, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare systems. From AI-powered diagnostics and personalized treatments to robotic surgery and drug discovery, the potential benefits of AI in medicine are immense. However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of the ethical, practical, and societal challenges that accompany its implementation.
As we’ve explored, key achievements include significant advancements in diagnostic accuracy, the development of personalized therapies tailored to individual patient needs, and the acceleration of drug discovery processes. AI is also streamlining administrative tasks, freeing up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. However, significant challenges remain. Protecting patient data privacy and security, mitigating bias in AI algorithms, ensuring transparency and explainability, navigating complex regulatory pathways, and addressing ethical dilemmas are crucial for building trust and maximizing the positive impact of AI in healthcare.
A balanced approach is essential. We must prioritize patient safety, ensure equitable access to AI-powered healthcare solutions, and address ethical concerns proactively. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, policymakers, and technology developers is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of AI in healthcare and ensuring that its benefits are shared by all.
Looking ahead, the future of AI in medicine is filled with promise. We can expect to see even more sophisticated applications emerge, including more personalized and proactive care through wearable devices and remote monitoring systems, expanded access to healthcare through telemedicine and AI assistants, and further acceleration of drug discovery and personalized treatments. As AI technology continues to advance, its impact on the quality and accessibility of medical care will only grow more profound, shaping a future where medicine is more precise, personalized, and accessible for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are some examples of how AI is being used in medical diagnostics?
AI is being used to analyze medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disease at earlier stages. It’s also being used to analyze biomarkers and genetic data to predict disease risk.
How does AI contribute to personalized medicine?
AI analyzes a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and medical history to develop individualized treatment plans and predict their response to different medications. This allows for more targeted therapies with fewer side effects.
How is AI accelerating drug discovery?
AI algorithms can analyze vast databases of molecular structures and biological data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety, significantly reducing the time and cost required to bring new drugs to market.
What are the main challenges associated with using AI in healthcare?
Some key challenges include ensuring data privacy and security, mitigating bias in AI algorithms, ensuring transparency and explainability, navigating regulatory approval processes, and addressing ethical dilemmas related to patient autonomy and algorithmic accountability.
How can we ensure the ethical use of AI in healthcare?
We must prioritize patient safety, ensure equitable access to AI-powered solutions, address ethical concerns proactively, and foster collaboration between researchers, clinicians, policymakers, and technology developers.
What is the future of AI in healthcare?
The future of AI in healthcare is promising, with potential for more personalized and proactive care through wearables and remote monitoring, expanded access to care through telemedicine, and accelerated drug discovery and personalized treatments.
Will AI replace doctors?
While AI can automate certain tasks and assist doctors in making better decisions, it is unlikely to completely replace human physicians. The human element of care, including empathy, communication, and complex decision-making, remains crucial in medicine.


